
For humans, physical health means a good body health, which is healthy because of regular physical activity (exercise), good nutrition, and adequate rest.
As a country's or region's people experience improved nutrition, health
care, standards of living and quality of life, their height and weight
generally increase.
In fact, most people, when asked for a definition of health talk about
physical health. Physical health relates to anything concerning our
bodies as physical entities. Physical health has been the basis for
active living campaigns and the many nutrition drives that have swept
the industrialized world. People are exposed to so much "physical
health" data these days that it is hard to decide what is relevant and
what is not.
Another term for physical health is physical wellbeing. Physical
wellbeing is defined as something a person can achieve by developing all
health-related components of his/her lifestyle. Fitness reflects a
person's cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, flexibility,
and body composition. Other contributors to physical wellbeing may
include proper nutrition, bodyweight management, abstaining from drug
abuse, avoiding alcohol abuse, responsible sexual behavior (sexual
health), hygiene, and getting the right amount of sleep.
Mental health

Mental health refers to people's cognitive and emotional well-being. A
person who enjoys good mental health does not have a mental disorder.
According to WHO, mental health is "a state of well-being in which
the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the
normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is
able to make a contribution to his or her community".
No matter how many definitions people try to come up with regarding mental health, its assessment is still a subjective one.
People have always found it easier to explain what mental illness is,
rather than mental health. Most people agree that mental health refers
to the "absence of mental illness". For some, this definition is not
enough. They argue that if you pick 100 people who do not suffer from
any mental disorder or illness that could be diagnosed by a
psychiatrist, some people within those 100 will be mentally healthier
than others. Most people also agree that mental health includes the
ability to enjoy life, the ability to bounce back from adversity, the
ability to achieve balance (moderation), the ability to be flexible and
adapt, the ability to feel safe and secure, and self-actualization
(making the best of what you have).
Determinants of health
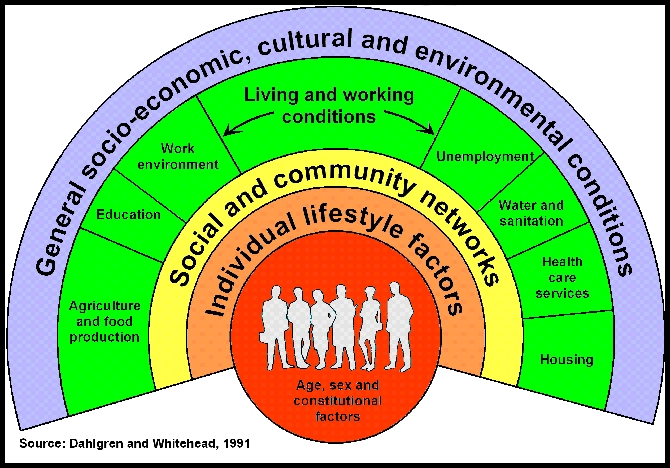
The health of individual people and their communities are affected by a
wide range of contributory factors. People's good or bad health is
determined by their environment and situations - what is happening and
what has happened to them, says WHO. WHO says that the following factors
probably have a bigger impact on our health than access and use of
health care services:
- Where we live
- The state of our environment
- Genetics
- Our income
- Our education level
- Our relationship with friends and family
WHO says the main determinants to health are:
- Our economy and society ("The social and economic environment")
- Where we live, what is physically around us ("The physical environment")
- What we are and what we do ("The person's individual characteristics and behaviors")
As our good health depends on the context of our lives, praising or
criticizing people for their good or bad health is wrong. Most of the
factors that contribute towards our good or bad health are out of our
control. According to WHO, these factors (determinants), include the
following, among others:
- Socioeconomic status - the higher a person's socioeconomic
status is, the more likely he/she is to enjoy good health. The link is a
clear one. Socioeconomic status affects all members of the family,
including newborn babies. An Australian study
found that women of lower socioeconomic status are less likely to
breastfeed their newborn babies - a factor which will have an impact on
the health of the baby just as he/she enters the world. A South Korean study revealed a clear link between low socioeconomic status and heart attack and stroke risk.
- Education - people with lower levels of education generally have a higher risk of experiencing poorer health. Their levels of stress will most likely be higher,
compared to people with higher academic qualifications. A person with a
high level of education will probably have higher self-esteem. A study carried out by researchers at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, found that elderly people who had a higher level of health literacy were more likely to live longer. Another study from San Francisco VA Medical Center found that Literacy at less than a ninth-grade level almost doubles the five-year risk of mortality among elderly people.
- Physical environment - if your water is clean and safe, the
air you breathe is pure, your workplace is healthy, your house is
comfortable and safe, you are more likely to enjoy good health compared
to somebody whose water supply is not clean and safe, the air he/she
breathes is contaminated, the workplace is unhealthy, etc. A study carried out by researchers at Zuyd University, The Netherlands, found that just an hour of sniffing car exhaust fumes induces a stress response in the brain's activity. Another study carried out at Indiana University-Purdue University
found that chronic lead poisoning, caused in part by the ingestion of
contaminated dirt, affects hundreds of thousands more children in the
United States than the acute lead poisoning associated with imported
toys or jewelry.
- Job prospects and employment conditions - if you have a job,
statistics show you are more likely to enjoy better health than people
who are unemployed. If you have some control over your working
conditions your health will benefit too. A study by researchers at State University of New York at Albany
found that workers who lost their job through no fault of their own
were twice as likely as continuously employed workers to report over the
next 18 months that they developed a new illness, such as high blood pressure, diabetes or heart disease.
- Support from people around you - if you have family support,
as well as support from friends and your community your chances of
enjoying good health are far greater than somebody who has none of these
things. A study carried out at the University of Washington
found that strong family support, not peer support, is protective in
reducing future suicidal behavior among young adults when they have
experienced depression or have attempted suicide.
- Culture - the traditions and customs of a society and how a
family responds to them play an important role in people's health. The
impact could be either good or bad for health. The tradition of genital
mutilation of women has an impact on infection rates and the mental
health of millions of girls and women in many countries. A study published in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health
found that when young people dress according to the customs of their
own ethnic group, they may be less likely to have mental health problems
later in life.
- Genetic inheritance - people's longevity, general health, and
propensity to certain diseases are partly determined by their genetic
makeup. Researchers from Vrije Universiteit, Holland, the Medical
College of Georgia, USA, and Duke University, USA
showed that people's genes play a key role in how they respond both
biologically and psychologically to stress in their environment.
- What we do and how we manage - what we eat, our physical
activity, whether or not we smoke or drink or take drugs, and how we
cope with stress play an important role on our physical and mental
well-being.
- Access and use of health services - a society that has access
and uses good quality health services is more likely to enjoy better
health than one that doesn't. For example, developed countries that have
universal health care services have longer life expectancies for their
people compared to developed countries that don't.
- Gender - men and women are susceptible to some different
diseases, conditions and physical experiences, which play a role in our
general health. For example, childbirth, ovarian cancer, and cervical cancer, are experienced only by women, while prostate cancer, testicular cancer
are only experienced by men. During wars more men than women tend to be
called up to fight, and subsequently become injured or die. Adult women
are more likely to be the physical victims of domestic abuse, compared
to adult men. In some societies women are not given the same access to
education as men - education is a factor that influences health. Many
studies have revealed gender disparities in healthcare services, even in developed countries.
What is wellness?
The term wellness was first used by a doctor called Halbert L. Dunn, USA, who published a small booklet entitled "High Level Wellness" in 1961. The term is much more widely used in North American than in the United Kingdom.
According to the Mickinley Health Center, University of Illinois, wellness "is
a state of optimal well-being that is oriented toward maximizing an
individual's potential. This is a life-long process of moving towards
enhancing your physical, intellectual, emotional, social, spiritual, and
environmental well-being."
The University of East Carolina defines wellness as "the integration
of mind, body and spirit. Optimal wellness allows us to achieve our
goals and find meaning and purpose in our lives. Wellness combines seven
dimensions of well-being into a quality way of living. Overall,
wellness is the ability to live life to the fullest and to maximize
personal potential in a variety of ways. Wellness involves continually
learning and making changes to enhance your state of wellness. When we
balance the physical, intellectual, emotional, social, occupational,
spiritual, and environmental aspects of life, we achieve true wellness."
According to Medilexicon's medical dictionary, wellness is "A
philosophy of life and personal hygiene that views health as not merely
the absence of illness but the full realization of one's physical and
mental potential, as achieved through positive attitudes, fitness
training, a diet low in fat and high in fiber, and the avoidance of
unhealthful practices (smoking, drug and alcohol abuse, overeating)".
Sources: National Health Service (NHS), UK, The Mayo Clinic, Wikipedia,
HHS (Department of Health and Human Services USA), NIH (National
Institutes of Health, USA).



No comments:
Post a Comment